A primary provider (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP, or Oracle) is required to connect Kubernetes costs. If you have on-premises costs you want to track, see the Enable On-Premises Support section below.
Agent Functionality
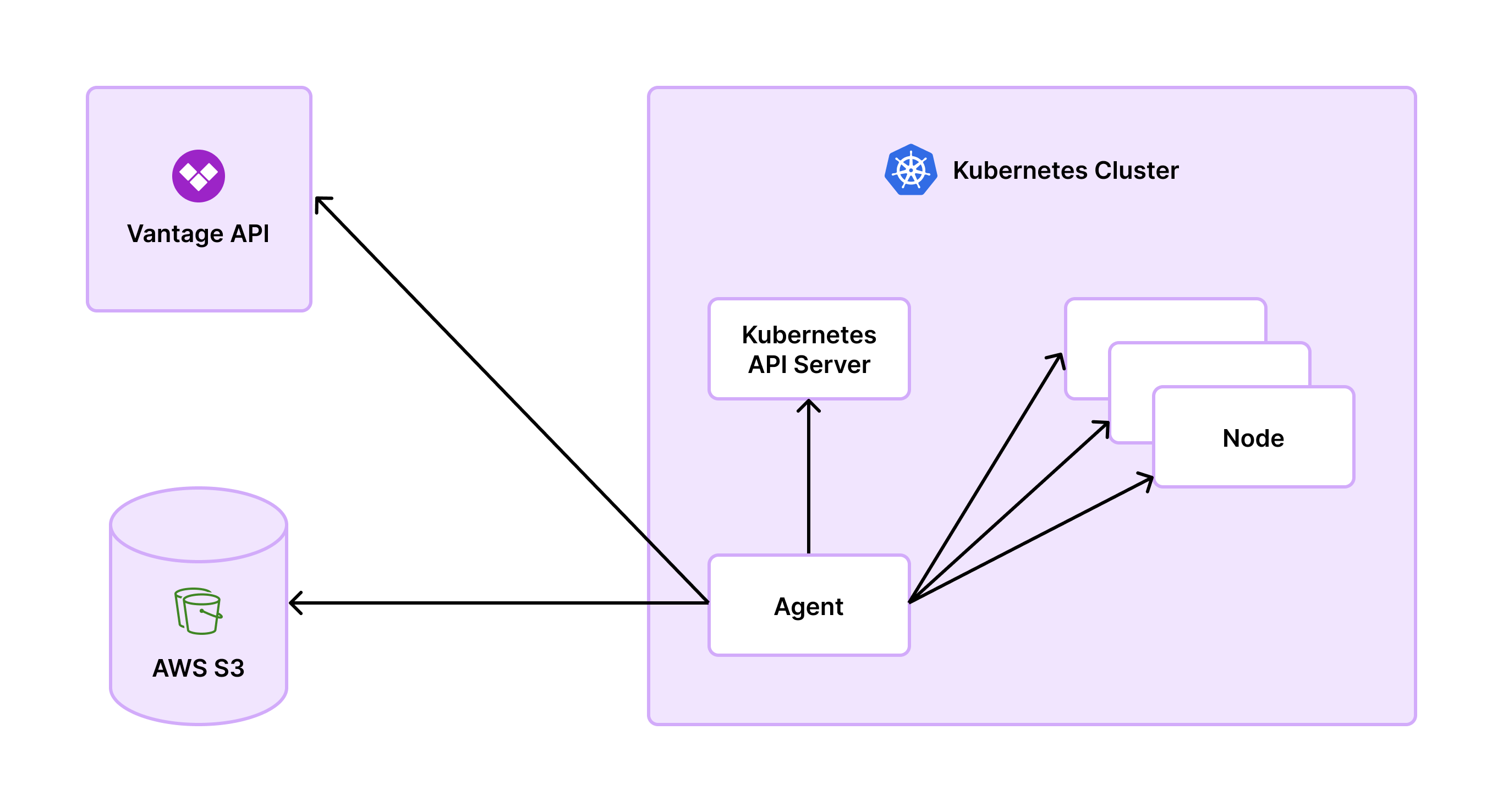
The Vantage Kubernetes agent relies on native Kubernetes APIs, such askube-apiserver for metadata and kubelet for container data. Access to these APIs is controlled via Kubernetes RBAC using a Service Account and ClusterRole included in the Vantage Kubernetes agent Helm chart.
Data is periodically collected and stored for aggregation, then sent directly to the Vantage service through an API, with your Vantage API token for authentication. This process avoids extra storage costs incurred by the OpenCost integration. The agent’s architecture eliminates the need for deploying OpenCost-specific Prometheus pods, which makes scaling easier.
The agent supports GPU cost monitoring and efficiency metrics. For detailed information on viewing GPU costs, configuring GPU metrics collection, and supported GPU instance types, see the Kubernetes GPU documentation.
Service Compatibility
The Vantage Kubernetes agent is compatible with the following services:- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes (OKE)
- Custom rates for on-premises services (see the Enable On-Premises Support section below)
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) Autopilot
For GKE Autopilot users, you don’t need to install the agent. These costs will already be present under Cost By Resource for the Kubernetes Engine service in a Cost Report.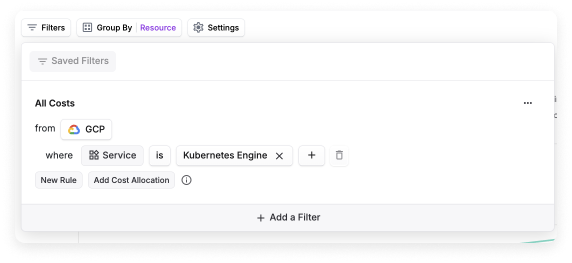
Install Vantage Kubernetes Agent
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required before you install the Vantage Kubernetes agent:- The Helm package manager for Kubernetes
kubectl- A running Kubernetes cluster
- An already connected primary provider (i.e., AWS, Azure, GCP, or Oracle Cloud, or on-premises)
- A Vantage API token with READ and WRITE scopes enabled (it’s recommended to use a service token rather than a personal access token)
- Important: For Enterprise accounts, the service token should be assigned to the Everyone team to obtain Integration Owner access. This is required for organization-level actions such as managing provider integrations, which the Kubernetes agent needs to function properly. Service tokens assigned to other teams will not have the necessary permissions for these organization-level operations.
- If you do not already have an integration enabled, navigate to the Kubernetes Integration page in the Vantage console, and click the Enable Kubernetes Agent button (you won’t need to do this for subsequent integrations)
- Review the section on Data Persistence before you begin
- Review the section on Naming Your Clusters
Create a Connection
The following steps are also provided in the Vantage Kubernetes agent Helm chart repository. See the Helm chart repository for all value configurations. If you would like to use a manifest-based option instead, see the section below
Install the
vantage-kubernetes-agent Helm chart. Ensure you update the values for VANTAGE_API_TOKEN (obtained in the Prerequisites above) and CLUSTER_ID (the unique value for your cluster).Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) Connections
If you are creating an AKS connection, you will need to configure the following parameters to avoid AKS-specific errors:- Set the
VANTAGE_KUBE_SKIP_TLS_VERIFYenvironment variable totrue. This setting is controlled byagent.disableKubeTLSverifywithin the Helm chart. For details, see the TLS verify error section. - Configure the
VANTAGE_NODE_ADDRESS_TYPESenvironment variable, which is controlled by theagent.nodeAddressTypesin the Helm chart. In this case, the type to use for your cluster will most likely beInternalIP. For configuration details, see the DNS lookup error section.
Naming Your Clusters
When you name your clusters, ensure the cluster ID adheres to Kubernetes object naming conventions. While the agent does not enforce specific formats, valid characters include:- Lowercase and uppercase letters (
a-z,A-Z) - Numbers (
0-9) - Periods (
.), underscores (_), and hyphens (-)
Enable Collection of Annotations and Namespace Labels
You can optionally enable the collection of annotations and namespace labels.- Annotations: The agent accepts a comma-separated list of annotation keys, called
VANTAGE_ALLOWED_ANNOTATIONS, as an environment variable at startup. To enable the collection of annotations, configure theagent.allowedAnnotationsparameter of the Helm chart with a list of annotations to be sent to Vantage. Note there is a max of 10 annotations, and values are truncated after 100 characters. - Namespace labels: The agent accepts
VANTAGE_COLLECT_NAMESPACE_LABELSas an environment variable at startup. To enable the collection of namespace labels, configure theagent.collectNamespaceLabelsparameter of the Helm chart.
Enable On-Premises Support
The Vantage Kubernetes agent supports on-premises Kubernetes clusters by allowing you to define custom cost rates for compute and storage resources. To enable on-premises cost tracking, you can define custom hourly rates for different resource types by adding annotations to your Kubernetes nodes. The agent supports the following annotation keys:ram_gb_hourly_rate- Cost per GB of RAM per hourgpu_gb_hourly_rate- Cost per GB of GPU memory per hourvcpu_hourly_rate- Cost per vCPU per hourstorage_gb_hourly_rate- Cost per GB of storage per hour
Only RAM and CPU are required.
agent.allowedAnnotations="ram_gb_hourly_rate,gpu_gb_hourly_rate,vcpu_hourly_rate,storage_gb_hourly_rate").
If a rate annotation is missing, Vantage will skip cost calculation for that specific resource. To maintain accurate visibility, we recommend applying all four annotation keys (ram, vcpu, gpu, storage) consistently across your on-prem nodes. Workload metrics are collected based on your configured polling interval (default: 60 seconds, minimum: 5 seconds), sent to Vantage hourly, and refreshed daily in the console. The agent’s data persistence feature retains data for up to 96 hours during connectivity issues.
To view on-prem costs, you can filter by cluster on Cost Reports, Kubernetes Efficiency Reports, and in Virtual Tags. Vantage will also provide Kubernetes Rightsizing Recommendations for on-prem workloads. Savings for these recommendations will be driven off of the custom rates you provide.
On-Premises Rate Calculation
If you know the total hourly cost of a host but need to derive per-resource rates, you can use the following normalization formula. This approach distributes the total cost proportionally across CPU, RAM, and GPU based on standard cloud pricing ratios.- Calculation steps
- Example
(Optional) Enable Collection of PVC Labels
This feature is available with Vantage Kubernetes agent
v1.0.30 and later.VANTAGE_COLLECT_PVC_LABELS as an environment variable at startup. To enable the collection of PVC Labels, set agent.collectPVCLabels to true in the agent’s Helm chart configuration. PVC Labels are collected from persistent volume claims associated with pods.
Manifest-Based Deployment Option
You can usehelm template to generate a static manifest via the existing repo. This option generates files (YAML) so that you can then decide to deploy them however you want.
Resource Usage
The limits provided within the Helm chart are set low to support small clusters (approximately 10 nodes) and should be considered the minimum values for deploying an agent. Estimates for larger clusters are roughly:- ~1 CPU/1000 node
- ~5 MB/node
--set flag. You can also include the values using one of the many options Helm supports:
Configure Polling Interval
To enable a configurable polling interval for the Vantage Kubernetes Agent, specify an
image.tag when you upgrade. Upgrade and deploy your Helm chart using the following command:helm repo update && helm upgrade -n vantage vka vantage/vantage-kubernetes-agent --set agent.pollingInterval={interval},image.tag={special-tag} --reuse-valuesagent.pollingInterval parameter of the Helm chart with the desired polling period in seconds, such as --set agent.pollingInterval=30 for a 30-second polling interval. If you enter a polling interval that is not in the list of allowed intervals, the agent will fail to start, and an error message is returned within the response.
There are performance implications on both the Kubernetes API server and the Vantage Kubernetes agent if you shorten the interval for when the Vantage Kubernetes agent polls the pods. Your polling interval should be based on the shortest-lived task within your cluster, and you should note how long it takes for the agent to scrape nodes. You can obtain this information using the vantage_last_node_scrape_timestamp_seconds metric provided by the agent.
It is recommended that you monitor system performance and adjust the interval as needed to balance granularity with resource usage.
Validate Installation
Follow the steps below to validate the agent’s installation.
Costs are exported from the cluster hourly and then made available nightly. It’s important to note that these costs might encounter delays based on their associated cloud integration’s cost data. For instance, if there is a one-day delay in an AWS Cost and Usage Report, the clusters dependent on that data will experience a similar delay.
Monitoring
The agent exposes a Prometheus metrics endpoint via the/metrics endpoint, exposed by default on port 9010. This port can be changed via the Helm chart’s service.port value.
The metrics endpoint includes standard Golang process stats as well as agent-related metrics for node scrape results, node scrape duration, internal data persistence, and reporting.
For users who want to monitor the agent:
vantage_last_node_scrape_count{result="fail"} should be low (between 0 and 1% of total nodes). Some failures may occur as nodes come and go within the cluster, but consistent failures are not expected and should be investigated.rate(vantage_report_count{result="fail"}[5m]) should be 0. Reporting occurs within the first 5 minutes of every hour and will retry roughly once per minute. Each failure increments this counter. If the agent is unable to report within the first 10 minutes of an hour, some data may be lost from the previous window, as only the previous ~70 data points are retained.Upgrade Agent
To see which version of the Kubernetes agent you are running:On the Manage tab, click the settings button (looks like a cog wheel) next to a specific integration.
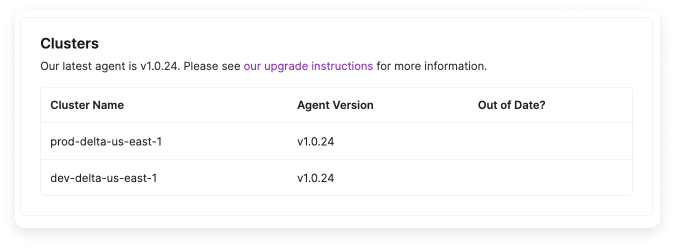
AKS users should remember to follow the AKS-specific instructions again when updating.
Data Persistence
The agent requires a persistent store for periodic backups of time-series data as well as checkpointing for periodic reporting. By default, the Helm chart configures the agent to use a Persistent Volume (PV), which works well for clusters ranging from tens to thousands of nodes. The Helm chart sets a defaultpersist.mountPath value of /var/lib/vantage-agent, which enables PV-based persistence by default. To disable PV persistence, set persist: null in your values.yaml.
If Persistent Volumes are not supported with your cluster, or if you prefer to centralize persistence, S3 is available as an alternative for agents deployed in AWS. See the section below for details. If you require persistence to a different object store, contact support@vantage.sh.
If both a Persistent Volume and an S3 bucket are configured, the agent will prioritize S3.
Persistent Metrics Recovery
Persistent Metrics Recovery is enabled by default in Kubernetes Agent version v1.0.29. (See the Upgrade the Agent section for details on how to upgrade your agent to the latest version.)
- Compresses the reports into a
.tararchive and moves them to a backup location, either:- A mounted volume in the container, or
- An S3 bucket you configure
- Retries the upload until successful or until the report is 96 hours old.
- Deletes old reports to manage disk space and avoid unbounded storage use.
This feature does not require additional configuration flags, but it does respect the
PERSIST_DIR or PERSIST_S3_BUCKET environment variables, if provided. If neither is set, the agent will not store hourly backups. For persistence configuration options, see the section above.Configure Agent for S3 Persistence
The agent uses IAM roles for service accounts to access the configured bucket. The defaultvantage namespace and vka-vantage-kubernetes-agent service account names may vary based on your configuration.
Below are the expected associated permissions for the IAM role:
- Environment variable: Set
VANTAGE_PERSIST_S3_BUCKETin the agent deployment. - Helm chart values:
$CLUSTER_ID/ prefix within the bucket. Multiple agents can use the same bucket as long as they do not have overlapping CLUSTER_ID values. An optional prefix can be prepended with VANTAGE_PERSIST_S3_PREFIX resulting in $VANTAGE_PERSIST_S3_PREFIX/$CLUSTER_ID/ being the prefix used by the agent for all objects uploaded.
Configure GPU Metrics
To track GPU utilization and idle costs for your Kubernetes workloads, enable GPU metrics collection in the Vantage Kubernetes agent. This section covers GPU setup for AWS and Azure, which use native cloud billing data combined with DCGM exporter metrics. For neocloud providers (DigitalOcean, CoreWeave, Nebius, etc.) that use annotation-based pricing, see the Enable Neocloud GPU Support section below.Step 1 - Configure the Agent
Install or upgrade to Vantage Kubernetes agent version 1.0.26 or later, available as part of Helm Chart version 1.0.34. To collect GPU metrics, set the following parameter totrue in the agent’s values.yaml: --set agent.gpu.usageMetrics=true.
The agent also provides some additional GPU configuration options. The defaults match the operator’s defaults. Refer to the agent’s values.yaml for option configuration details.
Step 2 - Configure the GPU Operator
For net-new installations:To configure the
dcgm-exporter to collect custom metrics, retrieve the metrics file and save it as dcgm-metrics.csv:Follow the steps provided in the NVIDIA GPU Operator installation guide to install the operator. Set the following options on the operator:
Enable Neocloud GPU Support
You must be on Vantage Kubernetes Agent version 1.2.0 (Helm Chart v1.4.0) or higher to enable neocloud support.
Step 1 - Verify DCGM Exporter is Running
The NVIDIA DCGM exporter must be running in your cluster. Many neocloud providers deploy this natively, so you may only need to verify it’s running. If your provider hasn’t deployed it, you can install it as part of the NVIDIA GPU Operator or independently. For instructions on installing the DCGM exporter from scratch, see Step 2 - Configure the GPU Operator in the Configure GPU Metrics section above. The DCGM exporter must expose theDCGM_FI_DEV_FB_USED and DCGM_FI_DEV_FB_FREE metrics. The agent currently expects DCGM_FI_DEV_FB_TOTAL to be present or the GPU’s total memory to be available from the provider. If you’re installing the exporter yourself, you can configure it to include DCGM_FI_DEV_FB_TOTAL (see the Configure GPU Metrics section).
Step 2 - Add GPU Rate Annotations to Nodes
Similar to on-premises clusters, you need to define custom GPU cost rates by adding annotations to your Kubernetes nodes. Add the following annotations to your node metadata:Only RAM and CPU are required for basic cost tracking, but GPU annotations are necessary for GPU cost allocation. If you know the total hourly cost of your host but need to derive per-resource rates, see the On-Premises Rate Calculation section for a normalization formula and examples.
Step 3 - Configure the Agent
Configure the agent to collect the annotations and enable GPU metrics collection. When installing or upgrading the agent, set the following parameters:- Collect the custom rate annotations from your nodes (via
agent.allowedAnnotations) - Enable GPU metrics collection (via
agent.gpu.usageMetrics)
Step 4 - Configure DCGM Exporter Connection (Optional)
If your neocloud provider has pre-deployed the DCGM exporter in a non-standard location (different namespace, service name, etc.), you may need to configure the agent to point to the correct exporter location. The agent uses default values that match the standard GPU operator deployment, so you only need to configure this if your provider’s exporter is deployed differently. The agent provides configuration options for the namespace, service name, port name, and path where the exporter is available. Configure these options in the agent’svalues.yaml:
agent.gpu.exporterNamespace- The namespace where the GPU exporter is deployed (default:gpu-operator)agent.gpu.exporterServiceName- The service name for the GPU exporter (default:nvidia-dcgm-exporter)agent.gpu.exporterPortName- The port name for the metrics port (default:gpu-metrics)agent.gpu.exporterPath- The path where the metrics endpoint is available (default:/metrics)
Common Errors
Failed to Fetch Presigned URL
Afailed to fetch presigned urls error can occur for a few reasons, as described below.
API Token Error
The below error occurs when the agent attempts to fetch presigned URLs but fails due to an invalidAuthorization header field value. The error log typically looks like this:
VANTAGE_API_TOKEN (obtained in the Prerequisites above) is valid and properly formatted. If necessary, generate a new token and update the configuration.
404 Not Found Error
The below error occurs when the agent attempts to fetch presigned URLs but fails due to the cluster ID potentially including invalid characters. The error log typically looks like this:Failed to Set Up Controller Store—MissingRegion
This error occurs when the agent cannot initialize the controller store due to missing or misconfigured AWS region settings. The error log will typically look like:
Verify the Service Account configuration:
- Check if the
eks.amazonaws.com/role-arnannotation is correctly added to the Service Account. Run the following command to inspect the configuration: - Ensure the Service Account matches the Helm chart settings in the agent’s
serviceAccountconfiguration block of the Helm chart values file. This is a name that you can also set within the file.
Ensure the IAM role is correctly set up:
- Review the AWS IAM Roles for Service Accounts documentation to confirm that the IAM role is configured with the necessary permissions and associated with the Service Account.
Configure S3 persistence:
- See the Agent S3 persistence setup section for details.
DNS Lookup Error
You may receive a DNS Lookup Error that indicates"level":"ERROR","msg":"failed to scrape node" and no such host.
The agent uses the node status addresses to determine what hostname to look up for the node’s stats, which are available via the /metrics/resource endpoint. This can be configured with the VANTAGE_NODE_ADDRESS_TYPES environment variable, which is controlled by the agent.nodeAddressTypes in the Helm chart. By default, the priority order is Hostname,InternalDNS,InternalIP,ExternalDNS,ExternalIP.
To understand which type to use for your cluster, you can look at the available addresses for one of your nodes. The type corresponds to one of the configurable nodeAddressTypes.
EOF Error When Starting
The agent uses local files for recovering from crashes or restarts. If this backup file becomes corrupted, most commonly due to OOMKill, the most straightforward approach to get the agent running again is to perform a fresh install or remove thePersistentVolumeClaim, PersistentVolume, and Pod.
An example error log line might look like:
helm, run:
TLS Verify Error When Scraping Nodes
The agent connects to each node to collect usage metrics from the/metrics/resources endpoint. This access is managed via Kubernetes RBAC, but in some cases, the node’s TLS certificate may not be valid and will result in TLS errors when attempting this connection. This most often affects clusters in AKS. To skip TLS verify within the Kubernetes client, you can set the VANTAGE_KUBE_SKIP_TLS_VERIFY environment variable to true. This setting is controlled by agent.disableKubeTLSverify within the Helm chart. This does not affect requests outside of the cluster itself, such as to the Vantage API or S3.
An example error log line might look like:
ERROR level messages appear:
Pod Scheduling Errors
The most common cause for pod scheduling errors is the persistent volume not being provisioned. By default, the agent is deployed as a StatefulSet with a persistent volume for persisting internal state. The state allows the agent to recover from a restart without losing the historical data for the current reporting window. An example error for this case would be present in the events on thevka-vantage-kubernetes-agent-0 pod and include an error that contains unbound immediate PersistentVolumeClaims.
The resolution to this error is based on the cluster’s configuration and the specific cloud provider. More information might be present on the persistent volume claim or persistent volume. For Kubernetes clusters on AWS, S3 can be used for data persistence.
Additional provider references are also listed here:
- GCP: Using the Compute Engine persistent disk CSI Driver
- Azure: Container Storage Interface (CSI) drivers on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
- AWS: Amazon EBS CSI driver
Volume Support Error
If you see an error related tobinding volumes: context deadline exceeded, this means you may not have volume support on your cluster. This error typically occurs when your cluster is unable to provision or attach persistent storage volumes required by your applications. Check your cluster’s configuration and ensure the storage provider is properly set up.
Missing Namespaces in Reports
If certain namespaces are not appearing in your Kubernetes reports, this typically indicates one of two issues:-
Verify agent installation on all clusters:
- Ensure the Vantage Kubernetes agent is installed and running on all clusters where you expect to see namespace data
- Check that the agent pod is running in each cluster:
- Verify the agent is properly configured with the correct
CLUSTER_IDfor each cluster. See the Naming Your Clusters section for details
-
Check agent logs for crashes and resource issues:
- Review the agent logs to ensure the agent is not crashing or running out of memory:
Replace
<pod-name>with your agent pod name (e.g.,vka-vantage-kubernetes-agent-0). - Look for
ERRORlevel messages indicating crashes, out-of-memory (OOM) kills, or repeated failures - If the agent is crashing or running out of memory, you may need to increase the resource limits. See the Resource Usage section for guidance on scaling resources based on your cluster size
- Review the agent logs to ensure the agent is not crashing or running out of memory:
Active Resources and Rightsizing Recommendations
Rightsizing recommendations require version 1.0.24 or later of the Vantage Kubernetes agent. See the upgrading section for information on how to upgrade the agent. Once the upgrade is complete, the agent will begin uploading the data needed to generate rightsizing recommendations. After the agent is upgraded or installed, recommendations will become available within 48 hours. This step is required to ensure there is enough data to make a valid recommendation. Historical data is not available before the agent upgrade, so it is recommended that you observe cyclical resource usage patterns, such as a weekly spike when you first review recommendations.
Migrate Costs from OpenCost to Vantage Kubernetes Agent
If you are moving from an OpenCost integration to the agent-based integration, you can contact support@vantage.sh to have your previous integration data maintained. Any overlapping data will be removed from the agent data by the Vantage team.Maintaining OpenCost Filters
If you previously used the OpenCost integration and are transitioning to the new agent-based integration, your existing filters will be retained. It’s important to note that in situations where labels contained characters excluded from Prometheus labels, such as-, the OpenCost integration received the normalized versions of those labels from Prometheus. The Vantage Kubernetes agent, on the other hand, directly retrieves labels from the kube-apiserver, resulting in more precise data. However, this change may necessitate updates to filters that previously relied on the normalized values. You can contact support@vantage.sh to have these filters converted for you.