- Kubernetes Cost Reports. Use Cost Reports to drill into costs by Cluster, Namespace, Service, and Label, as well as combine Kubernetes costs with other providers, such as a database or cache layer.
- Kubernetes Efficiency Metrics and Reports. Display the cost efficiency down to the pod level of a cluster. These metrics are useful for rightsizing and cost optimization. You can also create efficiency reports based on these metrics.
Kubernetes Cost Reports
Kubernetes Cost Reports provide cost visibility by Cluster, Label, Namespace, and Service. They include Kubernetes-specific filters and filter logic. You can combine specific Kubernetes costs with other services. In the below example, the filter includes the costs of a specific service with corresponding RDS database costs.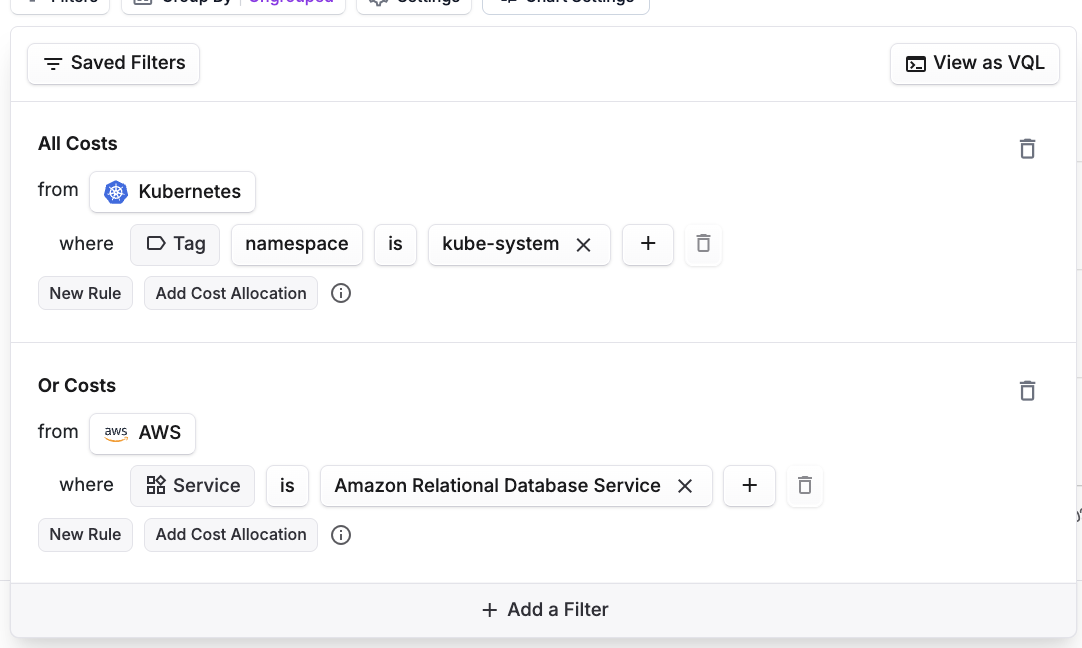
Additional Kubernetes Filters
Vantage provides advanced filtering and grouping options for Kubernetes Cost Reports and Efficiency Reports. These additional filters help you more accurately allocate and optimize Kubernetes spend.Filter by CPU, RAM, Storage, and GPU
On Kubernetes Cost Reports, you can also group and filter to see costs by CPU, RAM, storage, and GPU. To filter by these categories:Filter by PVC and Node Labels
PVC and Node Labels are key-value tags in Kubernetes. PVC Labels tag storage for filtering and grouping. Node Labels tag compute nodes to help with scheduling and analysis. You can use them to help you understand and filter usage by things like team, app, or environment.
pvc:xyz for PVCs and node:xyz for Nodes.
Node Labels are collected by default with the Vantage Kubernetes agent. See the Vantage Kubernetes agent documentation for information on how to configure the collection of PVC Labels.
- PVC Labels are collected from persistent volume claims associated with pods.
- Node Labels are collected from the nodes where pods are scheduled.
Cost Data Source
The costs displayed on these reports come from your integration with the Vantage Kubernetes agent. The agent calculates the cost of a running pod by analyzing the CPU, RAM, GPU, as well as storage usage and calculates the cost of each input based on the cost of the underlying infrastructure. Vantage uses a formula to divide the cost of a compute instance into CPU, RAM, and GPU and then computes the cost for each type of resource. The cost calculation reflects the exact runtime of each pod, down to the minute. This means if a pod runs for only 5 minutes within an hour, Vantage recognizes only 5 minutes of spend, rather than the full hour. All the cost allocation calculations are done locally in your cluster and make this data available for querying.Kubernetes costs are not included in monthly tracked infrastructure costs as they’re already captured from underlying EKS, GKE, AKS, or OKE costs.
Kubernetes Efficiency Metrics and Reports
The below sections describe how to view and create Kubernetes Efficiency Metrics and Reports.Discounts on Efficiency Reports
CPU/memory rates are based on the underlying instances the pod is scheduled on. In Kubernetes Efficiency Reports, this is the undiscounted rate of the instance. Discounts are not reflected on these reports due to the variable nature of how discounts are applied, making it difficult to make comparisons over time. You can view discounts on Kubernetes Cost Reports.View Kubernetes Efficiency Metrics
Navigate to the Kubernetes page in the Vantage console.
On the left navigation menu, select an option to view connected Clusters, Namespaces, or Labels. Each view contains a graph as well as a table with the following headings:
- Name: The name of the Cluster, Namespace, or Label you’re viewing.
- Idle Costs: A dollar value representation of the number of resources requested that are idle.
- Total Costs: A dollar value representation of the total cost of the resources.
- Cost Efficiency: The ratio of idle costs and total costs.
Filter a cluster’s efficiency metrics by date or resource:
- From the top right of the graph, change the date range to see how costs have changed over time.
- From the resource list below each chart, click the icons next to each resource to view different aggregations. Click the View on chart button to isolate that specific resource on the chart.
Create Efficiency Reports
With Kubernetes efficiency reports, you can filter your Kubernetes cost data and create reports based on these filters. You have the option to filter for costs by Cluster, Namespace, or Label.Labels will include namespace labels and annotations if enabled in your Vantage Kubernetes agent integration.
Navigate to the Kubernetes page in the Vantage console.
On the left navigation menu, select Efficiency Reports. All existing Kubernetes efficiency reports will be listed, along with who created the report as well as the date when the report was created.
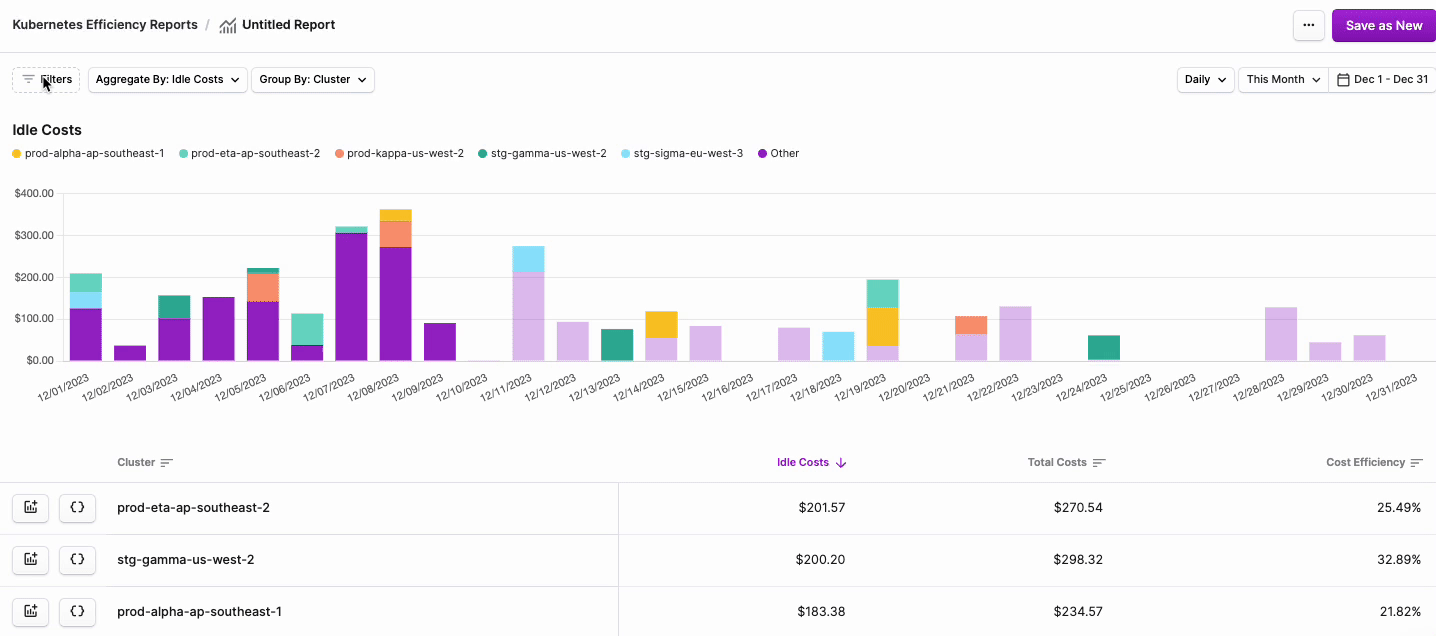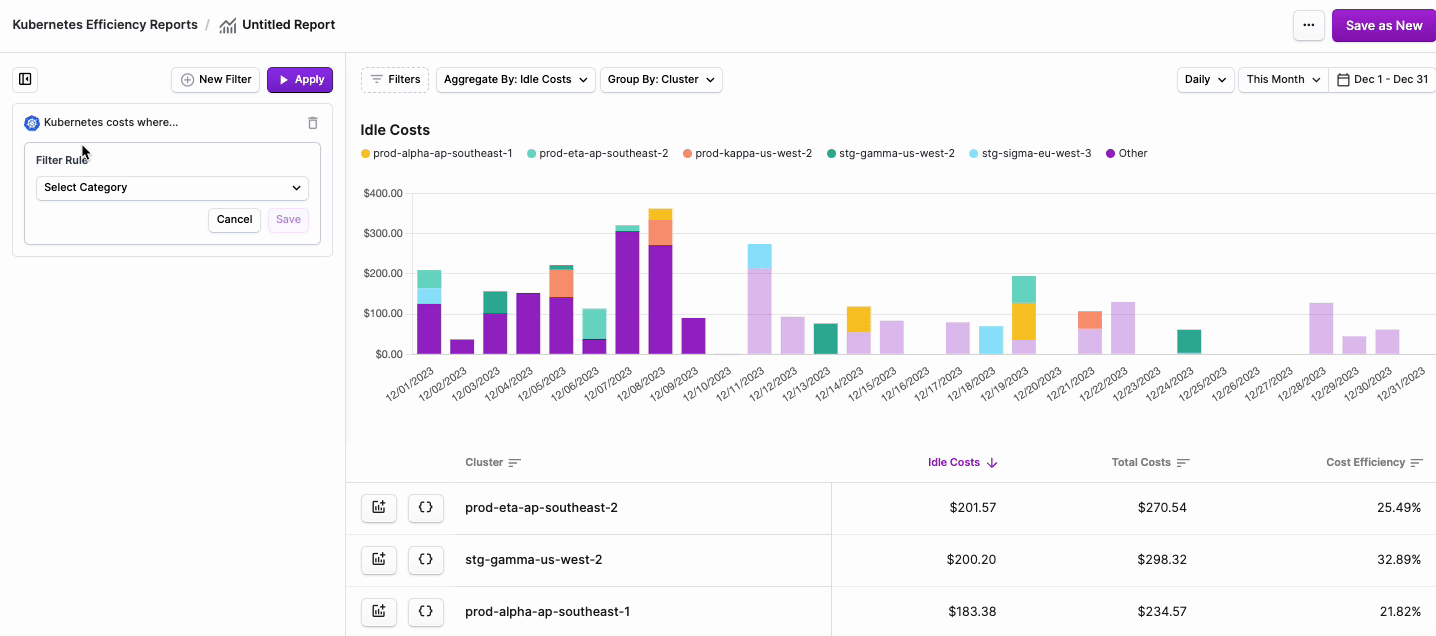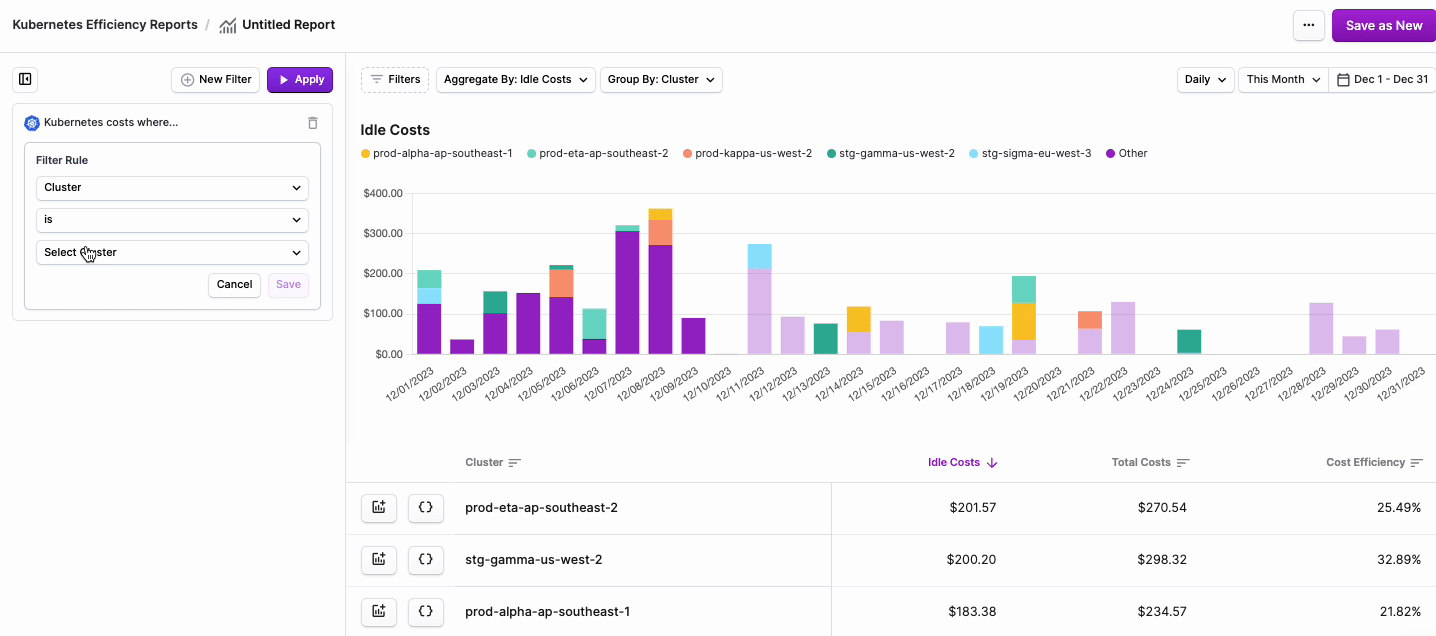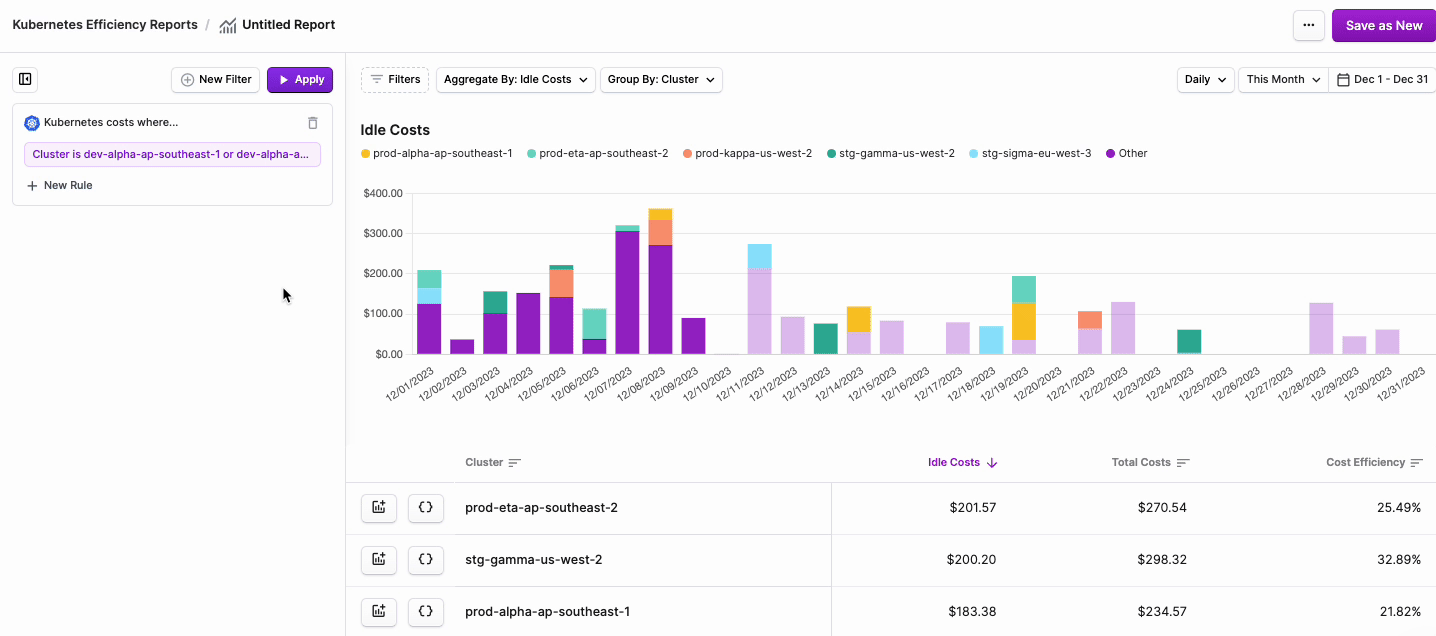
From the top right of the screen, click New Report. Like the efficiency metrics view, a chart/graph with idle costs is displayed. Below the chart, a table is displayed with the following columns: the resource’s name, Idle Costs, Total Costs, and Cost Efficiency.
To filter costs, click the Filters button on the top left of the chart.
- The Kubernetes costs where… tile is displayed. Click + New Rule.
-
From the filter dropdown menu, select either Cluster, Namespace, Category (cpu, ram, or gpu) or Label.
See the section below for information on how to enable GPU metrics.You can also filter by Node Labels, which are collected by the Vantage Kubernetes agent and appear as label filters in the format
node:xyz. Note that PVC Labels are not available for filtering on these reports. Kubernetes Efficiency Reports provide detail into the usage, efficiency, and cost of the underlying compute resources of Kubernetes Workloads. These reports do not include reporting on attached volume storage, where PVC Labels are applied. To report on both compute and storage resources, use Cost Reports. - Two additional dropdown menus are displayed. Select is or is not based on your desired filter criteria, then select one or more Clusters, Namespaces, or Labels from the second dropdown menu.
-
Click Save.
Click to view visual example
You can optionally edit your existing rule or add additional filter criteria.
- To edit the rule you just created, select the rule, make your changes, and click Save.
- If you want to add a rule to filter multiple criteria, such as filter by certain Clusters and another rule to filter by certain Namespaces, click + New Rule. Add the additional criteria and save.
- To add a separate rule set, click + New Filter. This rule set will be displayed as Or Kubernetes costs where… on the new tile.
- To delete a rule set, click the trashcan icon on the top right of the rule set.
Click to view visual example
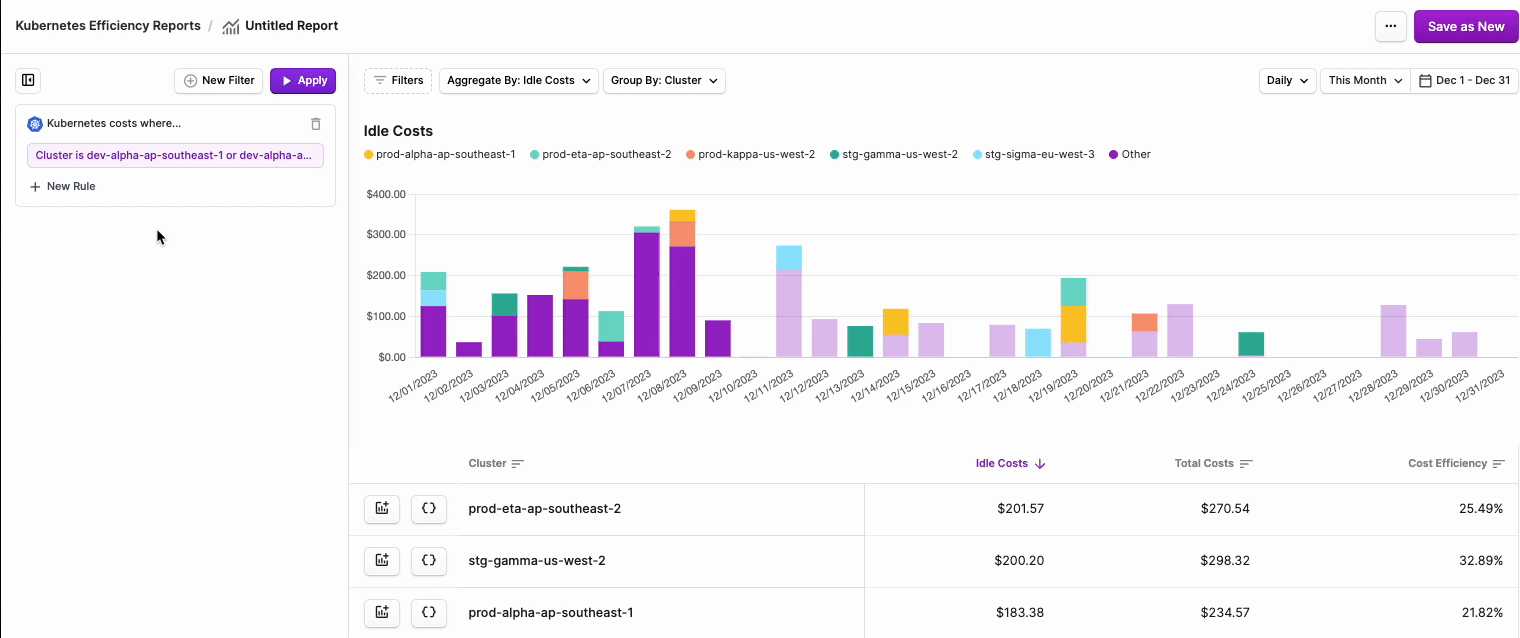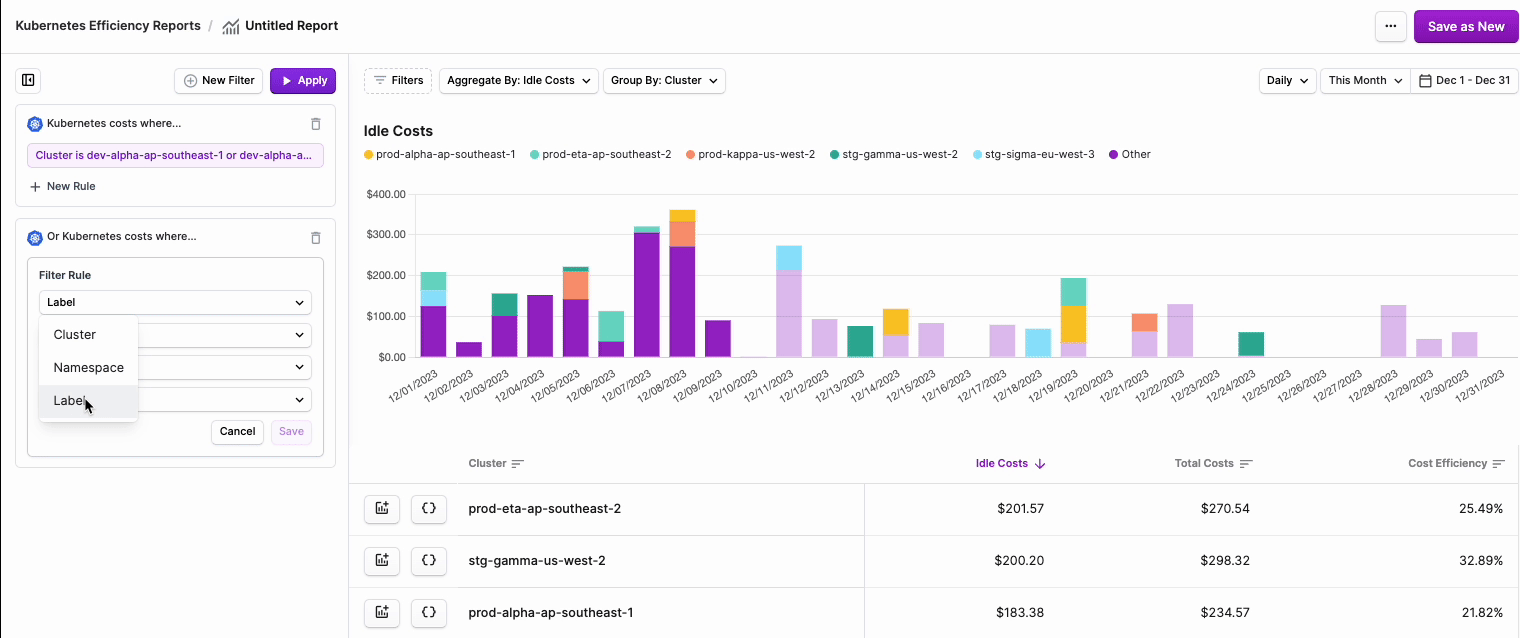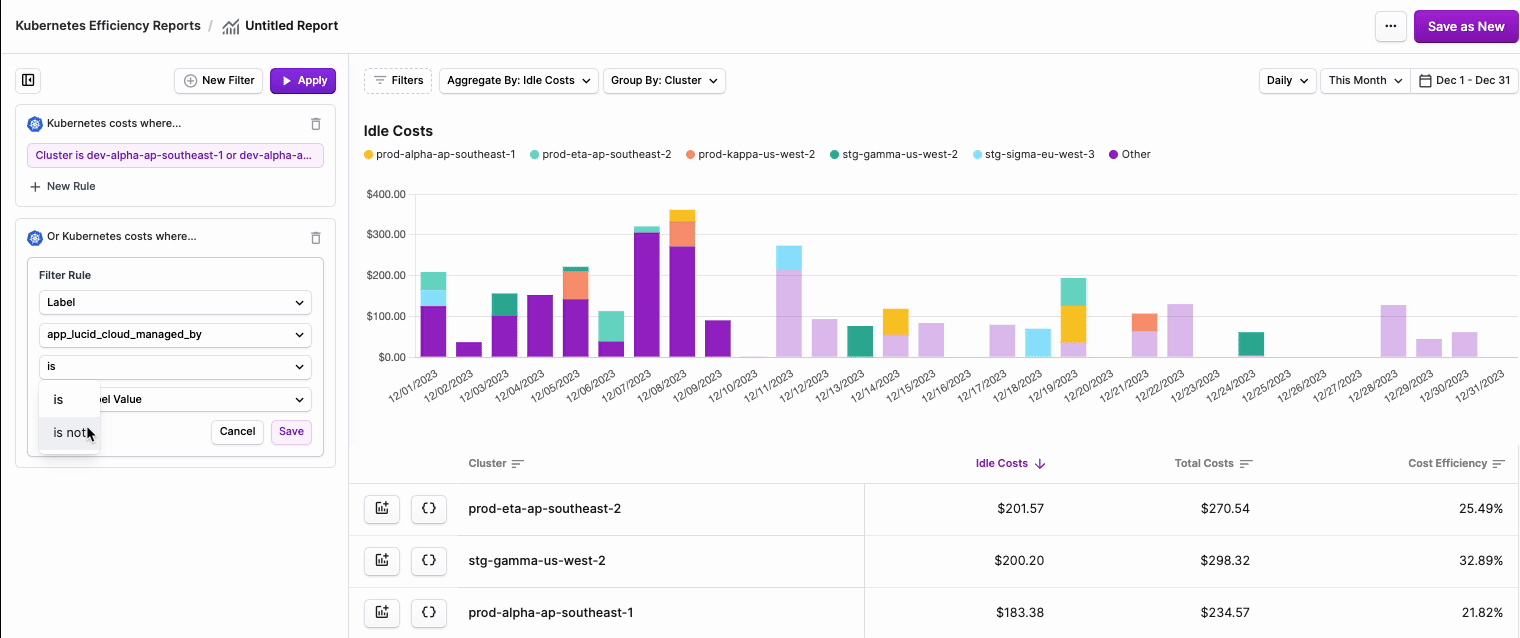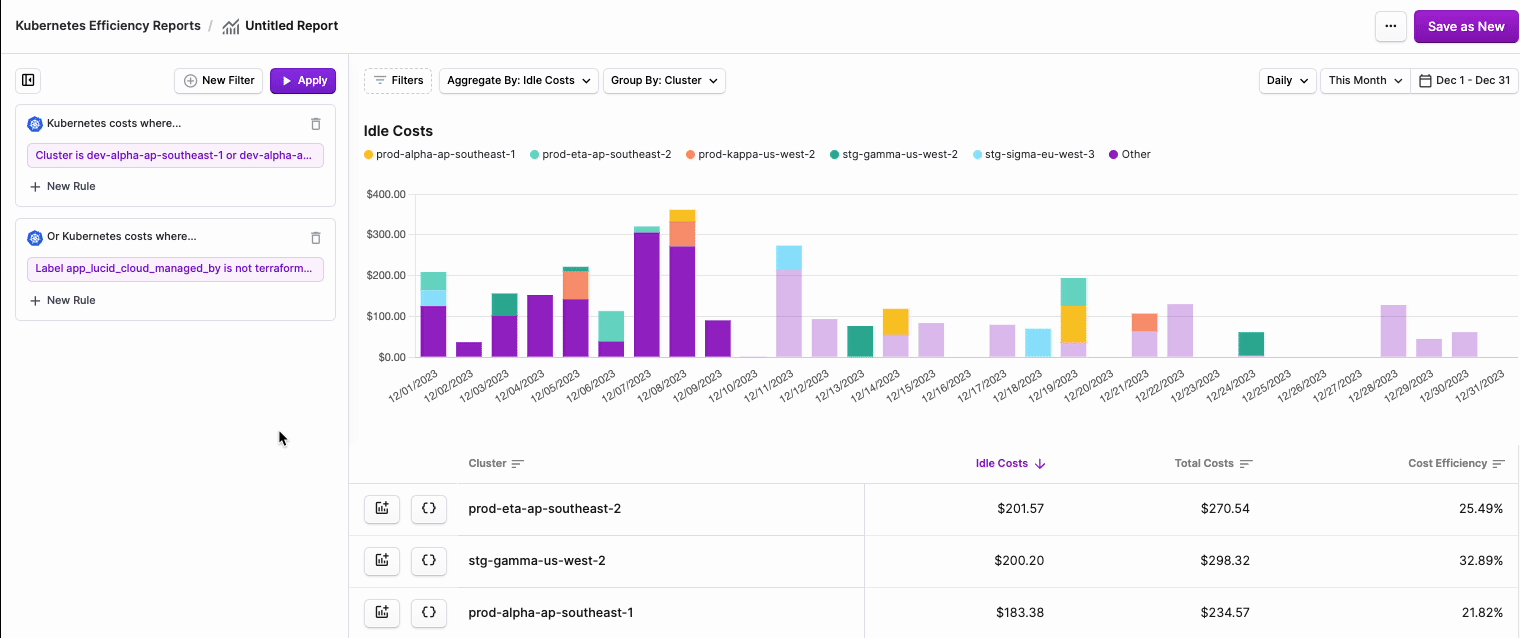
You have the option to further drill down into your costs.
- Above the graph, click the Aggregate By dropdown menu. Select either Idle Costs or Total Costs.
- To adjust aggregation dimensions, above the graph, click the Group By dropdown menu. Select one or more of the following options: Cluster, Namespace, and specific Label Key/Label Value.
- To adjust the date binning, select the menu on the top right of the graph. Select either Daily, Weekly, or Monthly.
- To change the date range, click the date picker menu on the top right of the graph and adjust the date range.
Click to view visual example
Add an Efficiency Report to a Dashboard
You can add your efficiency reports to dashboards. These reports will be displayed on the dashboard, along with other cost and segment reports.Select an existing dashboard, or click + New to create a new dashboard.
- If you are creating a new dashboard:
- Enter a Name.
- Under Add Reports, find and select your Kubernetes efficiency report.
- Click Save.
- If you want to add the report to an existing dashboard:
- From the top right of the existing dashboard, click Edit.
- Under Add Reports, find your efficiency report.
- Click Save.
Export Kubernetes Efficiency Reports
You can export your Kubernetes Efficiency Report as a CSV file for viewing outside the console.From the top right of any Kubernetes Efficiency Report, click the download icon (looks like an arrow with a line below it).
Select any Groupings that you want added as additional columns in the report (e.g., Cluster, Namespace). In addition, you can specify any Labels you want included.
Select or enter the emails for any users who you want to receive an emailed copy of the report.
Email recipients must be users in your Vantage organization.
For the Date Bin export option, when you select Week, the week in the export will begin on Monday, UTC. When you select Month, the month in the export will begin on the first of the month, UTC.
Efficiency Calculations
Pod resource efficiency is defined as the resource utilization versus the resource request over a given time window, prorated based on node uptime. These resource utilization metrics include CPU and RAM. When viewing efficiency, it will be shown as a percentage. 100% means the resource allocation is fully efficient. Idle costs are defined as the difference between the cost of requested resources (CPU and Memory) and the associated usage of those costs:Understanding the __idle__ Namespace in Kubernetes Efficiency Reports
When analyzing Kubernetes costs in Vantage, the __idle__ namespace represents the unallocated portion of nodes per hour, providing insight into overall cluster efficiency. The __idle__ namespace is included in total cluster costs.
As of March 2025, the
__idle__ namespace is enabled by default for new integrations. Existing integrations that have not already done so can contact support@vantage.sh to have the namespace enabled.__idle__ namespace costs, set the report’s Group By criteria to Namespace. In many cases, __idle__ ranks among the top namespaces in terms of cost. It highlights unused capacity in your cluster and helps identify opportunities for workload optimization.
__idle__ is calculated as the difference between a node’s total capacity and the sum of allocated pod resources. For example, if a node has:
- Total capacity:
8 CPU / 16 GB RAM - Pod usage:
8 CPU / 6 GB RAM
__idle__ are:
__idle__ costs should closely approximate total compute costs for the cluster. Minor discrepancies may occur due to hourly allocation calculations, such as multiple pods running at different times within an hour. In addition, if a node is fully allocated for a short period but mostly idle throughout an hour, __idle__ may not reflect partial usage, leading to some variation in reported costs.
Kubernetes GPU Idle Costs
For each Kubernetes pod, you can view the idle and total costs for NVIDIA GPU usage within a Kubernetes cluster. GPU memory usage is available on Kubernetes efficiency reports as an option for the Category filter and is included in the cost efficiency score per pod.How GPU Idle Costs Are Calculated
When an instance includes GPUs, 95% of the cost of the node will be allocated to the memory of the GPU. The number of GPUs requested by the pod will dictate how much of the total memory is allocated to the pod. Idle costs for allocated GPUs are determined by calculating the difference between the total allocated and the total used memory for the pod, down to the container level:- GPU utilization is not factored into the efficiency calculation; only GPU memory is tracked. If you have a workload that requires tracking GPU utilization, contact support@vantage.sh.
- At this time, only whole GPU requests are supported. If you use fractional GPUs and want those represented in cost monitoring, please contact support@vantage.sh.
Configure GPU Metrics
The Vantage Kubernetes agent automatically collects GPU usage information via the NVIDIA DCGM Exporter. The exporter is included as part of the NVIDIA GPU Operator, but it can also be installed independently. The agent scrapes the exporter directly and exposes the configuration for the namespace, service name, port name, and path. The default values are configured for the GPU operator default case. Vantage supports GPU cost monitoring for Kubernetes workloads. The setup process differs depending on your cloud provider:- AWS and Azure: GPU costs are automatically calculated from native cloud billing data combined with DCGM exporter metrics. See the Configure GPU Metrics section in the Kubernetes Agent documentation for setup instructions.
- Neocloud providers (DigitalOcean, CoreWeave, Nebius, etc.): GPU costs use annotation-based pricing similar to on-premises clusters. See the Enable Neocloud GPU Support section in the agent documentation.
View GPU Costs
Once GPU metrics are configured, GPU costs will appear in:- Kubernetes Efficiency Reports: Filter by
Category = gputo see GPU idle and total costs by cluster, namespace, or pod - Cost Reports: Filter and group by cluster, namespace, or labels to view GPU costs alongside other infrastructure costs
- Virtual Tags: Use GPU costs for cost allocation and chargeback
Kubernetes Rightsizing Recommendations
Vantage syncs Kubernetes managed workloads as active resources in your account. In cases where any of these workloads are identified to be overprovisioned, Vantage provides Kubernetes rightsizing recommendations. On the Kubernetes Efficiency Reports screen, a notification is displayed when rightsizing recommendations are available. Click Review Recommendations to view identified workloads.
Kubernetes Integration Method: The Vantage Kubernetes Agent
Agent usage data is uploaded several times throughout the day and updated within the Vantage platform nightly. However, Kubernetes costs will not be calculated until the costs from the cluster’s corresponding infrastructure provider are available. These costs might encounter delays based on their associated cloud integration’s cost data. For instance, if there is a one-day delay in an AWS Cost and Usage Report, the clusters dependent on that data will experience a similar delay. This often takes 48 hours to complete.Avoid Double Counting Costs in Cost Reports
When using the Vantage Kubernetes agent alongside your primary cloud provider (e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP), it’s important to ensure that costs are not double counted in your Cost Reports. The Kubernetes agent provides granular cost allocation at the pod, namespace, and cluster level, but these costs are derived from the underlying infrastructure costs that are already captured by your primary cloud provider. If you filter both by a primary provider (e.g., AWS) and Kubernetes, those costs will be double counted. Follow the steps below.Identify the underlying infrastructure type
Determine whether your Kubernetes deployment uses:
- Managed Kubernetes Service (i.e., EKS, AKS, GKE, OKS)
- Self-hosted Kubernetes (e.g., EC2 instances, virtual machines, bare metal)
Determine how to identify and isolate the infrastructure
- Managed Kubernetes Services
- Self-hosted Kubernetes
- Filter by cluster name tags: Cloud providers automatically tag resources with cluster names (e.g., for AWS
aws:eks:cluster-name) - Use node label tags: These are applied to underlying compute hosts and can be used to attribute compute costs based on infrastructure characteristics
Ensure you're comparing the same costs
When replacing cloud provider costs with Kubernetes agent costs, include idle costs to ensure an accurate comparison:
- The cloud provider bills you for the entire node, regardless of utilization
- The Kubernetes agent breaks down costs by actual usage (pods, namespaces, etc.)
- The
__idle__namespace is the difference between a node’s total capacity and the sum of allocated pod resources - To get a close comparison, include both the allocated costs and the idle costs from the Kubernetes agent
Troubleshooting Cost Discrepancies
If your costs don’t match between the Kubernetes agent and cloud provider data, consider the following options:- Check polling intervals: The agent polls every 60 seconds by default, but cloud providers may have different billing granularity. EKS is billed by the second, so short-lived pods may show different costs.
-
Verify instance mapping: Ensure the
node:provider_idtag correctly maps Kubernetes nodes to cloud provider instances. You can group by this tag in Cost Reports to cross-reference specific instances. This tag is available for filtering and grouping in Cost Reports (e.g., where Tagnode:provider_idis). - Account for storage costs: Use PVC labels to track storage costs separately.
- Consider purchase options: The Kubernetes agent uses on-demand pricing for consistency, while your actual costs may include Reserved Instances or Savings Plans. This is intentional to provide apples-to-apples comparisons.
-
Include idle costs: Ensure you’re including the
__idle__namespace when comparing total costs between sources.