Unit Costs
A unit is any metric that your business tracks, such as users, requests, transactions, customers, vendors, and so on. Unit costs can help you analyze the cost of goods sold (COGS). You can add unit costs as a visualization on Cost Reports to visualize your cloud infrastructure costs on a per unit basis. Business metrics are the units of data from your business that are aggregated and combined with costs to produce per unit costs on Cost Reports. By importing these business metrics into Vantage, you can track unit costs, like cost per daily active user, COGS per customer, cost per million API requests, etc.
In the visual example below, the business metric Per Requests per Second is visualized in the graph as a red line alongside daily costs. You can use this visualization to understand how changes in the request metric contribute to changes in your costs.
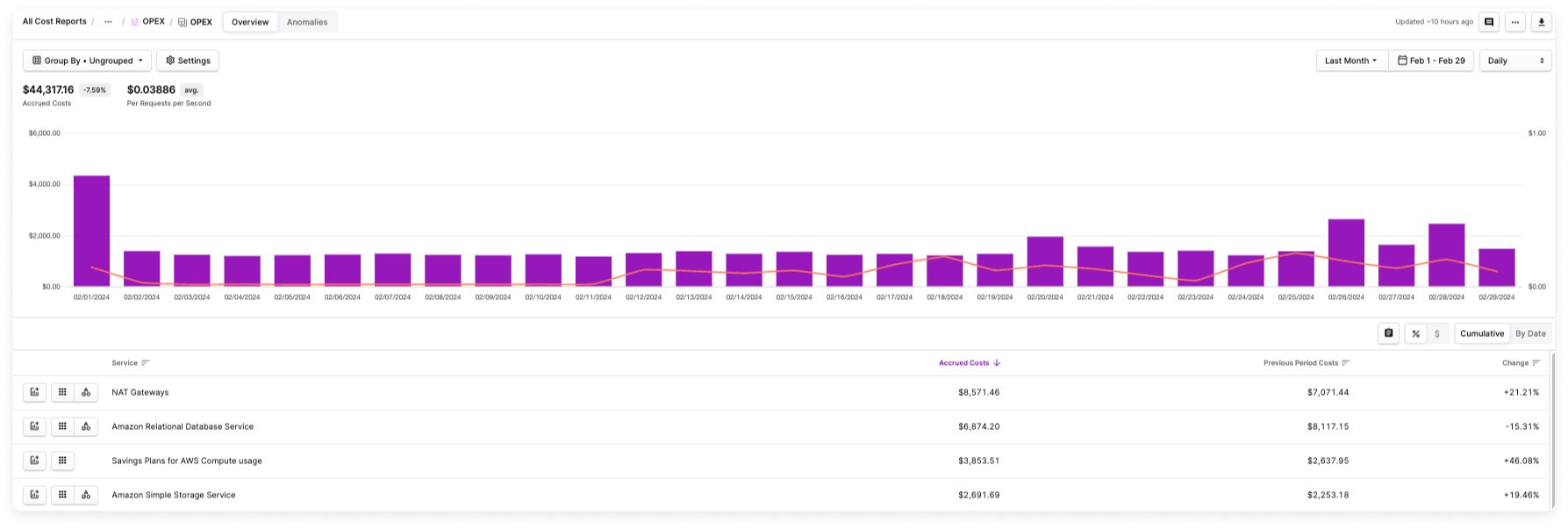
Labeled Business Metrics
You can optionally include a label for each uploaded metric. The label identifies the source of the metric—like an associated application or cost center. For example, a metric like Monthly Active Users typically applies to more than one application. The ability to allocate these metrics is important for analyzing both overall user activity and individual application performance, enabling more informed decision-making at the application level.
In the above example, you can create labels like Active Users App A, Active Users App B, etc. When you assign this metric to a Cost Report, you can decide which labels to include on the Cost Report and in the per unit cost calculation. Any labels you decide to include will be aggregated in the per unit cost calculation. So, in this example, if you decide to include only data with the Active Users App A label, then unit costs will be calculated only for that set of data. If you also include Active Users App B, then the per unit cost calculation will aggregate both sets of labeled data.
Import Business Metrics
To get started with business metrics and unit costs, you can also view a video demo on Vantage University 🎓.
Business metrics can be imported from other systems directly into Vantage and analyzed alongside cost data. You can create automatic import integrations with Amazon CloudWatch, manually import these metrics from a CSV file, or automatically upload metrics via the Vantage API.
The following steps are for importing via CloudWatch or a CSV file. If you want to automatically import metrics, see Import via the Vantage API.
- From the top navigation, click Financial Planning.
- On the left navigation, click Business Metrics. All existing business metrics are displayed. You can edit or delete business metrics from this screen.
- From the top right of the screen, click New Business Metric.
- Enter a business metric Title and click Create Business Metric.
- The Business Metrics screen is displayed:
- In the Assigned Cost Reports section, you can select one or more Cost Reports where the business metric will be displayed. See the Assign Business Metrics to Cost Reports section for details.
- In the Import Business Metrics section, you can import business metrics from a CSV file, Amazon CloudWatch, or Datadog.
Import from a CSV File
You can upload a CSV file that uses the following three-column format. This CSV file can replace existing data or be used to import new data.
The date column must be in YYYY-MM-DD format. The amount column must be a number. The label column is optional. See the section above for more information about labels.
A label can be added once per date.
date,amount,label
2024-01-09,295,app1
2024-01-16,909,app1
2024-01-23,934,app1
2024-01-30,772,app1
2024-01-09,344,app2
2024-01-16,789,app2
2024-01-23,922,app2
2024-01-30,768,app2
...
Click Upload a CSV. Select the CSV file and upload. After the file is imported, a dropdown menu for each month is displayed. For months with imported metrics, the date and associated metric number are displayed. Months with no metrics are blank.
Click to view visual example
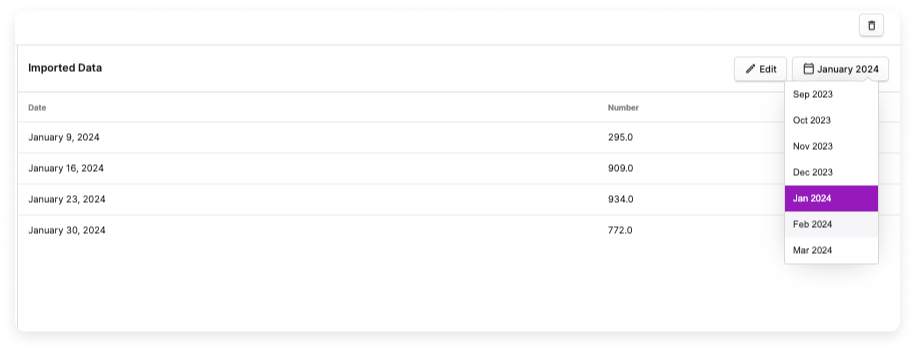
To add additional metrics or change the value of a metric, update your source CSV file. Then, click Edit and upload the edited file. The new or updated metric is displayed in the table. See the Assign Business Metrics to Cost Reports section for the next steps.
Import from Amazon CloudWatch
To import business metrics from Amazon CloudWatch, you need a specific metric name and AWS account, as described below. Ensure AWS is one of your connected providers
If Vantage does not have a Cross-Account IAM Role associated with your AWS account, you need to create one. See the AWS integration documentation for details.
- From the Import Business Metrics section, click Import via CloudWatch.
- For AWS Account, select the connected AWS account you want to import metrics from.
- Select an AWS Region.
- Enter a Namespace. A complete list of available namespaces can be found in the AWS documentation for AWS services that publish CloudWatch Metrics. Namespaces start with
AWS/followed by the service name (e.g.,AWS/EC2). - Enter a Metric name. Each AWS service has metrics that it sends to CloudWatch. Available metrics can be found in CloudWatch or the AWS documentation.tip
The AWS documentation includes a list of available metrics for services. For example, you can view EC2 instance metrics. An example metric to track in this instance is
CPUUtilization. For Amazon RDS, an example metric to track isWriteIOPSorReadIOPS. - For Dimensions, enter a Name and Value. Dimensions are used to pull specific statistical data for a metric. For example, enter
InstanceIdwith a value ofi-1234567890abcdef0. Each CloudWatch metric has a set of dimensions you can select. Click + Add a Dimension to add more than one dimension. - For each import, you must specify the Aggregation function to be used because metrics will be aggregated to the day. Select either Sum, Average, Maximum, or Minimum.
- Optionally, enter a dimension name for the Label Dimension field.
- Click Import Data.
Click to view visual example

The metrics will be automatically synced, daily, along with cost data from other integrations. See the Assign Business Metrics to Cost Reports section for the next steps.
Import from Datadog
To import business metrics from Datadog, ensure Datadog is one of your connected providers. If you do not have Datadog as one of your connected providers, you will be prompted to connect your Datadog account the first time you try to create a metric.
From the Import Business Metrics section, click Import via Datadog.
For Account, select the connected Datadog account for which you want to import metrics. If this is your first Datadog metric, you may be prompted to reauthorize your Datadog credentials and the required scopes for Vantage (i.e.,
billing_read,usage_read,metrics_read, andtimeseries_query scopes).For Raw Query, enter your Datadog metric, including aggregation, rollup formula, and label filters, into the text field. Your syntax should be similar to the following example:
aws.applicationelb.request_count{availabilityzone:us-east-1c, region:us-east-1}infoThe minimum aggregation for business metrics is daily. If you enter a lower granularity than daily, Vantage will perform aggregation at the daily level. For more information on the Datadog filtering syntax, see the Datadog documentation.
Click Import Data.
Click to view visual example

The metrics will be automatically synced, daily, along with cost data from other integrations. See the Assign Business Metrics to Cost Reports section for the next steps.
Import via the Vantage API
You can import business metrics to Vantage, from other applications, with the Vantage API. Use the /business_metrics endpoint to view, create, update, and delete business metrics.
The basic steps for using this endpoint are provided below. See the API documentation for details on parameters, sample requests, and sample responses.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have a valid Read/Write Vantage API token.
Create a Business Metric
The following example shows how to create a business metric by sending a POST request to the /business_metrics endpoint.
curl --request POST \
--url https://api.vantage.sh/v2/business_metrics \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <AUTH_TOKEN>' \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '
{
"title": "API Requests",
"cost_report_tokens_with_metadata": [
{
"unit_scale": "per_unit",
"cost_report_token": "rprt_12abc345def678gh"
}
],
"values": [
{
"date": "2024-02-01",
"amount": 1512,
"label": "app1"
},
{
"date": "2024-02-01",
"amount": 1816,
"label": "app2"
},
{
"date": "2024-02-02",
"amount": 1236,
"label": "app1"
},
{
"date": "2024-02-02",
"amount": 1711,
"label": "app2"
}
]
}
'
titleis a string that represents the business metric title (e.g.,RequestsorCPUUtilization).cost_report_tokens_with_metadatais an array of objects that represents one or more Cost Reports you want the business metric to be added to.cost_report_tokenis the uniquetokenfor the Cost Report.tipYou can access
cost_report_tokensvia the/cost_reportsendpoint.- The
unit_scaledetermines the scale of the business metric's values within the Cost Report. It has a default value ofper_unit. Other options includeper_hundred,per_thousand,per_million, andper_billion.
valuesis an array of objects that comprises thedateandamountkey/value pairs associated with each business metric data point.dateneeds to be inYYYY-MM-DDformat.amountneeds to be a number.labelis an optional field. See the section above for details.
The following JSON is returned in a successful 201 response, which includes the unique business metric token. Dates in the response are displayed in ISO 8601 format.
{
"token": "bsnss_mtrc_ab12345cde67fg8",
"title": "API Requests",
"created_by_token": "usr_0a123456789abcde",
"cost_report_tokens_with_metadata": [
{
"cost_report_token": "rprt_12abc345def678gh",
"unit_scale": "per_unit"
}
],
"values": [
{ "date": "2024-02-01T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1512.0", "label": "app1", },
{ "date": "2024-02-02T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1816.0", "label": "app2" },
{ "date": "2024-02-03T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1236.0", "label": "app1" },
{ "date": "2024-02-03T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1711.0", "label": "app2" },
]
}
Update a Business Metric
If you need to update or add additional data to a business metric, send a PUT request to the /business_metrics/{business_metric_token} endpoint. In the below example, an additional month of data is added to the business metric that was previously created. The request url includes the unique business metric token, received in the response from the POST call, to update the data.
curl --request PUT \
--url https://api.vantage.sh/v2/business_metrics/bsnss_mtrc_ab12345cde67fg8 \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <AUTH_TOKEN>' \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '
{
"values": [
{"date": "2024-03-01", "amount": 1743},
{"date": "2024-03-02", "amount": 1356},
{"date": "2024-03-03", "amount": 1563}
]
}
'
The following JSON is returned in a successful 201 response.
{
"token": "bsnss_mtrc_ab12345cde67fg8",
"title": "API Requests",
"created_by_token": "usr_0a123456789abcde",
"cost_report_tokens_with_metadata": [
{
"cost_report_token": "rprt_12abc345def678gh",
"unit_scale": "per_unit"
}
],
"values": [
{ "date": "2024-02-01T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1512.0" },
{ "date": "2024-02-02T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1816.0" },
{ "date": "2024-02-03T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1236.0" },
{ "date": "2024-03-01T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1743.0" },
{ "date": "2024-03-02T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1356.0" },
{ "date": "2024-03-03T00:00:00Z", "amount": "1563.0" }
]
}
You can also upload data via a CSV. Send a PUT request to the /business_metrics/{business_metric_token}/values.csv endpoint using the business metric’s token. Specify a path to the CSV in the csv parameter.
curl --request PUT \
--url https://api.vantage.sh/v2/business_metrics/bsnss_mtrc_ab12345cde67fg8/values.csv \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <AUTH_TOKEN>' \
--header 'content-type: multipart/form-data' \
--form 'csv=@<PATH_TO_CSV>'
Additional API Actions
To get all business metrics your API token has access to, send a GET request to the endpoint.
curl --request GET \
--url https://api.vantage.sh/v2/business_metrics \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <AUTH_TOKEN>'
You can also specify a specific business metric token in the url to get data for only one business metric.
curl --request GET \
--url https://api.vantage.sh/v2/business_metrics/bsnss_mtrc_ab12345cde67fg8 \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <AUTH_TOKEN>'
If you want to remove values for certain dates, you can pass an empty value as the amount for that date. Send a PUT request to the /business_metrics/{business_metric_token} endpoint using the business metric’s token. In the below example, an existing amount is removed for March 10th.
curl --request PUT \
--url https://api.vantage.sh/v2/business_metrics/bsnss_mtrc_ab12345cde67fg8 \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <AUTH_TOKEN>' \
--header 'content-type: application/json' \
--data '
{
"values": [
{
"date": "2024-03-10T00:00:00Z",
"amount": null
}
]
}
'
If you want to completely delete a business metric, send a DELETE request to the /business_metrics endpoint, and specify the token for the business metric you want to delete in the url.
curl --request DELETE \
--url https://api.vantage.sh/v2/business_metrics/bsnss_mtrc_ab12345cde67fg8 \
--header 'accept: application/json' \
--header 'authorization: Bearer <AUTH_TOKEN>'
Keep in mind that the DELETE action is permanent, and you will no longer have access to that business metric or see it displayed on corresponding reports.
Assign Business Metrics to Cost Reports
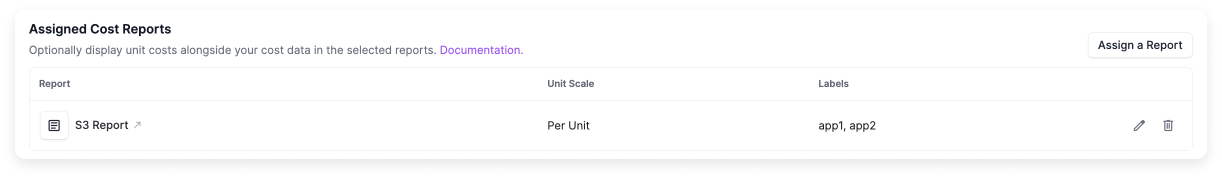
Once your import is complete you can assign metrics to one or more Cost Reports. You can also assign as many different business metrics to a Cost Report as you want.
- Under Assigned Cost Reports, click Assign a Report.
- The Assign a Report popup window is displayed. In the Report dropdown menu, search for and select a Cost Report.
- For Unit Scale, select either Per Unit, Per Hundred, Per Thousand, Per Million, or Per Billion. The scale is used to divide the business metric before calculating the cost per unit. Use this scale to create a per-unit cost, such as Cost per Thousand Requests. If you select Per Unit, no division occurs, and the actual metric number will be used within the Cost Report.
- For Label Filter, select any labels that were imported with your data.
- Any selected labels will be aggregated and applied to the Cost Report to calculate the per unit costs. For example, if you select the labels
app1andapp2, the per unit cost calculation will be an aggregate of the corresponding values for those labels. If you select onlyapp1, then the per unit cost calculation will only apply to values that correspond with theapp1label. - You can also select the unlabeled option, which includes any values that don't have a corresponding label.
- Any selected labels will be aggregated and applied to the Cost Report to calculate the per unit costs. For example, if you select the labels
- Click Save. The metric is displayed on the corresponding Cost Report based on the selected scale and optionally selected labels.
View Per Unit Costs on Cost Reports
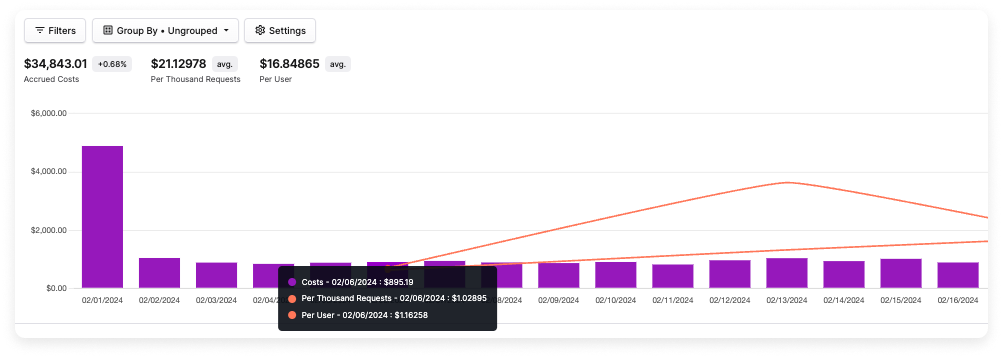
To inspect your unit costs, navigate to the assigned Cost Report. The average unit cost for the date range selected is displayed at the top of the screen.
To see the cost per unit line, ensure your view is set to daily, weekly, or monthly.
Hover over a data point to see the cost per unit for that day, week, or month. If you add multiple business metrics to the same Cost Report, each business metric is displayed as a separate line, as shown in the example above.