How It Works
Snowflake Compute is billed only when a query is running, rounded up to the hour; however, if multiple queries are running simultaneously, the cost is still only reported for that hour. This shared credit pool makes it difficult to understand which individual queries are contributing the most to costs. Each day, Vantage ingests the compute credits used, and their equivalent cost, and assigns a weighted cost to each query based on the total duration for which the query ran. For example, if you had 3 queries that ran for 1, 2, and 3 minutes respectively, and a total bill of $500, the query that ran for 3 minutes would be assigned a cost of $250 as it accounted for half of the overall query time.Grouping Queries
Vantage groups queries based on the source and structure of a query, so users can easily identify it. To determine the source, Vantage looks at the warehouse in which the query was run as well as the user who ran the query. To determine the structure of a query, Vantage will strip all query values and the order of columns and generate a normalized, unique fingerprint for the query.Viewing the Costs
Query costs are available in two views: on Cost Reports and in Active Resources.Query Costs in Cost Reports
To view query costs on a Cost Report:In the console, navigate to Cost Reports.
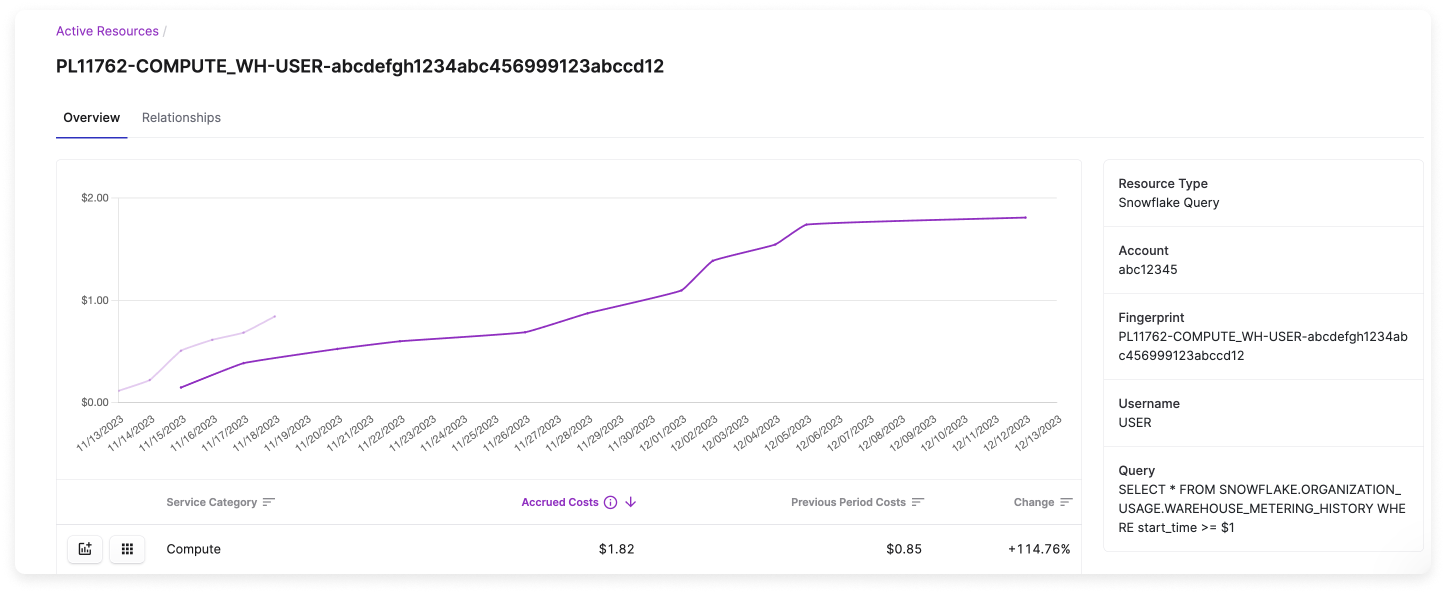
Query Costs in Active Resources View
To view query costs in the Active Resources view:Navigate to the Active Resources page in the console.
Security
Vantage ensures that any sensitive data contained in queries is never stored in Vantage systems. When theQUERY_HISTORY view is queried from Snowflake, that data is immediately processed to strip all values from queries before they are stored.